Fluorescence Microscopy: In-Line Illumination with Imaging Filters
Advancements in camera technology have revolutionized microscopy in biological and industrial applications. Biologists or engineers no longer need to spend hours tediously looking through eyepieces, constantly adjusting focus. Today, simplifying the recording and analysis of data is done with digital video microscope systems. For general information on this type of system, please view Digital Video Microscope Objective Setups.
To really see the benefit of a digital video microscope system, consider a configuration utilizing in-line illumination and filtering for optimal contrast and emission quantification.
THE BASICS OF FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY
Fluorescence microscopy is ideal for measuring and analyzing the absorption and excitation of various wavelengths of light. An in-line fluorescence microscopy setup utilizes a plate beamsplitter to redirect light from an illuminator into the parallel optical path. Mechanically, this setup is less complex than some other digital video microscope systems, and follows closely with Figure 1. Like most optical systems, this system begins with a sensor, an optical component, and an object under inspection. For the purposes of this discussion, #59-367 EO-3112C ½" CMOS Color USB Camera is used for the sensor in addition to #59-877 10X EO M Plan Apo Infinity-Corrected Objective and #54-774 MT-1 Accessory Tube Lens for the optical components. #54-774 is a type of accessory lens required to form an image from the infinity-corrected objective. The object under inspection can include such items as biological samples, plants or insects, glass or metal materials for inspection, and targets.
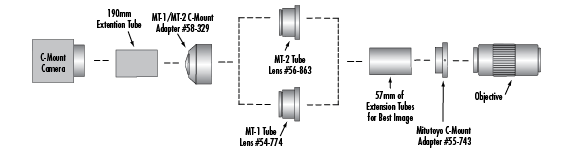
Figure 1: Seven-Component Infinity-Corrected Digital Video Microscope System for Fluorescence Microscopy
The choice of optical filters is important when selecting the excitation and emission wavelengths in the digital video microscope system from Figure 1. With the addition of optical filters, this type of setup is more commonly referred to as a fluorescence microscope (Figure 2), which is the backbone for more advanced techniques such as confocal, multiphoton, and Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. For in-depth information on the type of optical filters, please view Fluorophores and Optical Filters for Fluorescence Microscopy.
Blocking certain wavelengths allows one to bombard a sample with an excessive amount of light – samples typically imaged under a fluorescence microscope require a large amount of excitation energy to emit a quantifiable amount of light. Hard-coated filters with high optical densities and dichroic filters block certain wavelengths quickly and easily. The dichroic and emission filters are the two most crucial filters in the system. The dichroic filter reflects shorter wavelengths that typically excite fluorophores, and transmits longer wavelengths that are emitted. Together these optical filters prevent non-emission energy and stray light from reaching the sensor. The important parameters of a filter include the center wavelength (CWL), minimum transmission percentage, optical density (OD), and bandwidth, which at times can also be referred to as the full width at half maximum (FWHM). For more information on filters, please view to Optical Filters.
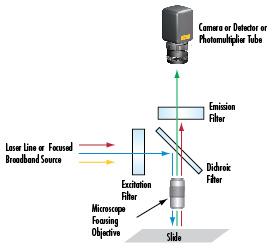
Figure 2: Basic Optical Filtering Arrangement for Fluorescence Microscopy
OPTICAL AND MECHANICAL COMPONENTS
There is a variety of optical, imaging, and positioning components needed to create a precision fluorescence microscopy setup. To make the selection process as easy as possible, Table 1 includes a complete component list (known as a bill of materials) detailing suggested products, their stock numbers, and their quantities.
Figure 3 illustrates a real-world setup with products from Table 1. From top to bottom, the assembly starts with #59-367 EO-3112C ½" CMOS Color USB Camera, and continues with #58-329 and #55-743 C-mount adapters which connect the #54-774 MT-1 Accessory Tube Lens. The space after the tube lens and prior to the objective is the parallel optical path, which is the benefit of an infinity-corrected system. This optical path allows for the introduction of optical components without distortion or aberrations. In Figure 3, #56-658 6 Position Filter Wheel Assembly holds a number of bandpass emission filters, and a dichroic beamsplitter which reflects white light downward for in-line illumination and cleans up the unwanted light being transmitted back through the objective to the sensor. Lastly, #59-877 10X EO M Plan Apo Infinity-Corrected Objective along with the series of mechanical components bring the sample into best focus. Figure 4 provides a closer look at the filter wheel assembly and placement after the tube lens.
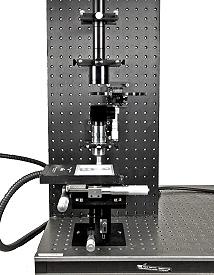
Figure 3: Sample Fluorescence Microscope Setup

Figure 4: Close-Up of Filter Wheel Assembly and Bandpass Filters in Parallel Optical Path